Newsletter 27: Understanding the Body’s Organ Systems
Introduction :
The human body is an intricate system made up of ten major organ systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining health and balance. These systems—such as the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems—work together to perform essential functions like transporting oxygen and nutrients, removing waste, defending against disease, and coordinating movement and thought. Understanding how each system functions helps us appreciate how the body stays alive, adapts, and heals itself daily.
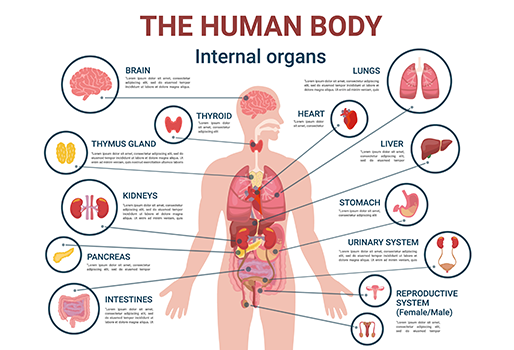
Our bodies are incredible, complex organisms made up of multiple organ systems that work together in harmony. Think of them as interconnected networks—each one with specific roles, yet all deeply reliant on one another to keep us alive and well. In the hierarchy of life, organ systems sit between individual organs and the entire organism, forming a crucial bridge in the body’s structure.
There are ten major organ systems in the human body, each comprising specific organs that carry out essential functions—from circulating blood to processing nutrients, eliminating waste, and regulating hormones. Learning how these systems interact not only deepens our understanding of human biology, but also empowers us to care for our health in a more informed way.
Here’s a brief overview of the 10 major organ systems in the human body and their key functions:
- Circulatory System
Function: Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body using the heart, blood, and blood vessels. - Respiratory System
Function: Enables breathing by exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment through the lungs and airways. - Digestive System
Function: Breaks down food into nutrients the body can absorb and eliminates solid waste; includes the stomach, intestines, liver, and more. - Nervous System
Function: Controls body functions and processes sensory information using the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. - Muscular System
Function: Facilitates movement, posture, and heat production through skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. - Skeletal System
Function: Provides structure, support, and protection for internal organs and stores minerals; includes bones, joints, and cartilage. - Endocrine System
Function: Regulates hormones and body processes such as growth, metabolism, and mood through glands like the thyroid and adrenal glands. - Immune/Lymphatic System
Function: Defends the body against infections and disease using white blood cells, lymph nodes, and lymphatic vessels. - Excretory (Urinary) System
Function: Removes waste and excess fluids from the blood through the kidneys, bladder, and associated ducts. - Reproductive System
Function: Enables reproduction and the production of hormones related to sexual development and function.
Summary:
Each organ system in the human body plays a unique yet interconnected role in keeping us alive, healthy, and functioning. When one system is out of balance, it can affect the others—highlighting the importance of holistic care for our entire body. By understanding how these systems work together, we gain valuable insight into maintaining our well-being and making more informed health choices.
